Understanding COPD Treatment Strategies
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) affects millions of Americans, making effective treatment strategies essential for managing symptoms and improving quality of life. Modern COPD treatment involves a comprehensive approach that combines medication, oxygen therapy, pulmonary rehabilitation, and lifestyle modifications. Healthcare providers work closely with patients to develop personalized treatment plans that address individual needs and disease progression stages.
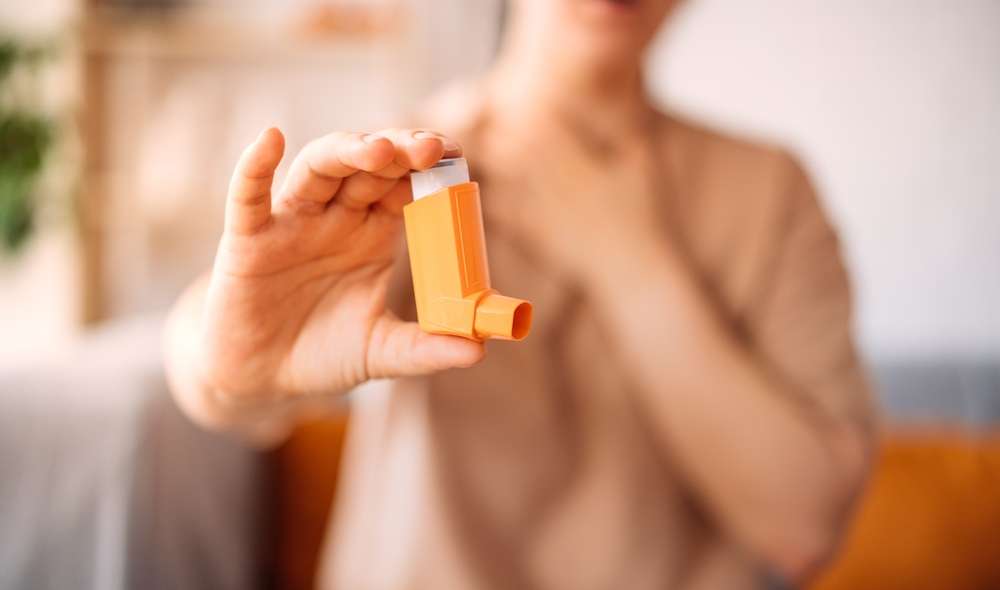

COPD treatment has evolved significantly over the past decades, offering patients multiple therapeutic options to manage their condition effectively. The disease, which includes emphysema and chronic bronchitis, requires a multifaceted approach that addresses both immediate symptom relief and long-term disease management. Treatment success depends on early diagnosis, patient compliance, and regular monitoring by healthcare professionals.
Understanding COPD Treatment Approaches
Effective COPD management begins with understanding the different treatment approaches available. The primary goal is to slow disease progression, reduce symptoms, and prevent complications. Treatment strategies typically fall into four main categories: bronchodilator therapy, anti-inflammatory medications, oxygen supplementation, and rehabilitation programs. Each approach targets specific aspects of the disease, working together to provide comprehensive care.
Healthcare providers assess disease severity using spirometry tests and symptom evaluations to determine the most appropriate treatment combination. The Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease (GOLD) guidelines help standardize treatment approaches, ensuring patients receive evidence-based care regardless of their healthcare provider.
Medication and Medical Interventions
Medication forms the cornerstone of COPD treatment, with several drug classes available to address different symptoms. Bronchodilators, including beta-2 agonists and anticholinergics, help open airways and improve breathing. Short-acting bronchodilators provide quick relief during symptom flare-ups, while long-acting versions offer sustained improvement throughout the day.
Inhaled corticosteroids reduce airway inflammation and are often combined with bronchodilators for enhanced effectiveness. Phosphodiesterase-4 inhibitors represent a newer class of medications that help reduce inflammation and may decrease exacerbation frequency. Some patients may require oral corticosteroids during severe flare-ups, though long-term use is generally avoided due to side effects.
Antibiotics play a crucial role in treating bacterial infections that can worsen COPD symptoms. Preventive vaccinations, including annual flu shots and pneumonia vaccines, help reduce the risk of respiratory infections that could trigger exacerbations.
Oxygen Therapy
Oxygen therapy becomes necessary when COPD progresses to the point where blood oxygen levels remain consistently low. This treatment involves supplemental oxygen delivery through nasal cannulas, masks, or portable concentrators. Long-term oxygen therapy can improve survival rates and quality of life for patients with severe COPD and chronic hypoxemia.
Patients typically undergo arterial blood gas testing or pulse oximetry monitoring to determine oxygen therapy needs. The prescription specifies flow rates and usage duration, which may range from nighttime-only use to continuous 24-hour supplementation. Modern portable oxygen concentrators allow patients to maintain active lifestyles while receiving necessary oxygen support.
Oxygen therapy requires careful monitoring to ensure appropriate dosing. Too little oxygen fails to provide benefits, while excessive oxygen can potentially suppress the respiratory drive in some COPD patients. Regular follow-up appointments help healthcare providers adjust oxygen prescriptions as the disease progresses.
Role of Pulmonary Rehabilitation
Pulmonary rehabilitation programs combine exercise training, education, and behavioral interventions to improve COPD management. These comprehensive programs typically last 6-12 weeks and include supervised exercise sessions, breathing techniques training, and nutritional counseling. Participants learn energy conservation strategies and proper inhaler techniques while building physical endurance.
Exercise components focus on both cardiovascular fitness and strength training, adapted to individual capabilities and limitations. Breathing exercises, including pursed-lip breathing and diaphragmatic breathing, help patients manage shortness of breath more effectively. Educational sessions cover disease management, medication adherence, and recognizing early signs of exacerbations.
Research consistently demonstrates that pulmonary rehabilitation reduces hospitalizations, improves exercise tolerance, and enhances overall quality of life. Many insurance plans cover these programs when prescribed by healthcare providers, making them accessible to most COPD patients.
| Treatment Type | Provider/Option | Cost Estimation |
|---|---|---|
| Bronchodilator Inhalers | Albuterol/Spiriva | $50-300 per month |
| Oxygen Concentrator | Inogen/Philips Respironics | $200-600 monthly rental |
| Pulmonary Rehabilitation | Hospital-based programs | $150-300 per session |
| Combination Medications | Symbicort/Advair | $200-400 per month |
Prices, rates, or cost estimates mentioned in this article are based on the latest available information but may change over time. Independent research is advised before making financial decisions.
Successful COPD treatment requires ongoing collaboration between patients and healthcare teams. Regular monitoring, medication adjustments, and lifestyle modifications all contribute to optimal disease management. While COPD cannot be cured, proper treatment strategies can significantly slow disease progression and help patients maintain active, fulfilling lives. Early intervention and consistent adherence to treatment plans remain the most important factors in achieving positive outcomes.
This article is for informational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. Please consult a qualified healthcare professional for personalized guidance and treatment.