Your Complete Guide to 5G Industrial IoT
You’ve heard about 5G and the Internet of Things, but how do they combine to revolutionize the industrial world? This guide breaks down exactly what 5G Industrial IoT is, exploring the profound impact it’s having on factory workflows, supply chains, and, most importantly, worker safety.
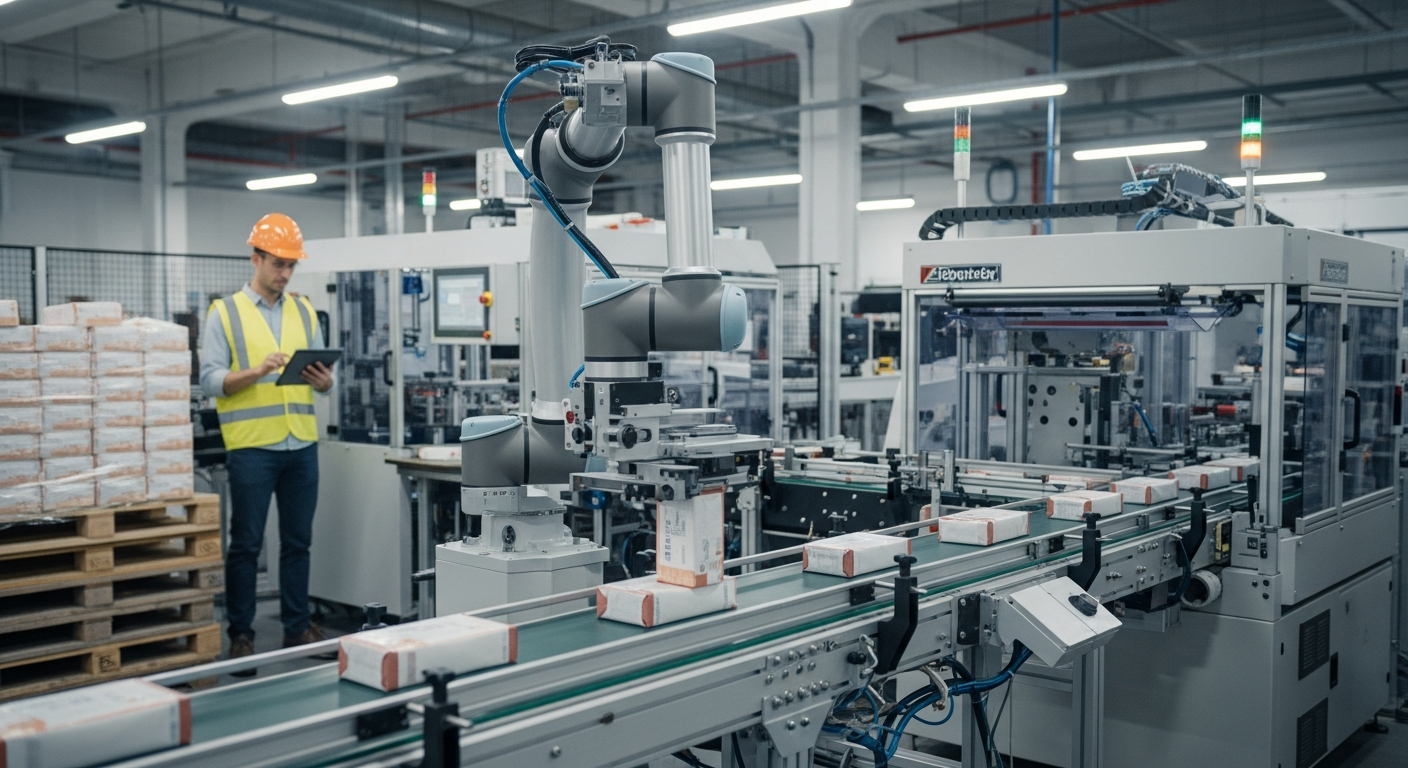

Manufacturing and industrial sectors are experiencing a technological revolution driven by the integration of 5G networks with Industrial Internet of Things systems. This combination delivers unprecedented speed, reliability, and connectivity that traditional wireless networks cannot match. Understanding how this technology works and its practical benefits helps organizations make informed decisions about modernizing their operations.
What is 5G Industrial IoT?
5G Industrial IoT refers to the application of fifth-generation cellular network technology to connect industrial devices, sensors, machinery, and systems within manufacturing and production environments. Unlike consumer-focused IoT applications, industrial implementations demand higher reliability, lower latency, and the ability to support thousands of simultaneous connections. The 5G standard provides data transmission speeds up to 100 times faster than 4G networks, with latency reduced to as low as one millisecond. This enables real-time communication between devices, supporting applications like predictive maintenance, automated quality control, and synchronized production lines. Industrial facilities deploy private 5G networks or utilize network slicing from carriers to ensure dedicated bandwidth and enhanced security for their operations.
How 5G IIoT Improves Industrial Workflows
The integration of 5G technology into industrial workflows creates measurable improvements across multiple operational dimensions. Real-time data collection from sensors embedded in production equipment allows immediate detection of anomalies, reducing unplanned downtime by enabling predictive maintenance schedules. Machine vision systems powered by 5G connectivity can analyze product quality at production speed, identifying defects that human inspectors might miss. Automated guided vehicles and robotic systems communicate seamlessly across factory floors, coordinating movements and optimizing material handling without collision risks. Warehouse operations benefit from connected inventory tracking systems that update stock levels instantaneously, improving supply chain accuracy. The enhanced bandwidth supports augmented reality applications that provide technicians with hands-free access to repair manuals and remote expert guidance during complex maintenance procedures. These workflow enhancements translate to reduced operational costs, improved product quality, and faster time-to-market for manufactured goods.
Remote Operation of Heavy Machinery
One of the most significant applications of 5G Industrial IoT involves enabling operators to control heavy machinery from remote locations. Mining operations, construction sites, and hazardous environments particularly benefit from this capability. Operators stationed in control centers can manage excavators, cranes, and drilling equipment through high-definition video feeds and haptic feedback systems that transmit tactile sensations. The ultra-low latency of 5G networks ensures that control inputs translate to machine movements with minimal delay, maintaining the precision required for complex tasks. This technology improves worker safety by removing personnel from dangerous environments while maintaining operational efficiency. Remote operation also allows skilled operators to manage multiple machines across different sites, optimizing labor resources. Telecommunications providers and equipment manufacturers have conducted successful trials demonstrating remote operation of construction equipment over distances exceeding several hundred miles, proving the viability of this approach for various industries.
Connected Worker Technology
The concept of connected workers represents a fundamental shift in how industrial personnel interact with their environment and each other. Wearable devices equipped with 5G connectivity provide workers with real-time access to operational data, safety alerts, and communication tools. Smart helmets display augmented reality overlays showing equipment status, procedural guidance, and hazard warnings directly in the worker’s field of vision. Biometric sensors monitor vital signs and fatigue levels, alerting supervisors to potential health risks before incidents occur. Location tracking systems ensure that personnel remain in safe zones and can be quickly located during emergencies. These connected systems facilitate collaboration between field workers and remote experts, enabling immediate problem-solving without production delays. Training programs benefit from immersive simulations that workers can access through connected devices, accelerating skill development while reducing training costs. The data collected from connected worker systems also provides insights into workflow efficiency, helping organizations identify bottlenecks and optimize task assignments.
Frequently Asked Questions
Organizations considering 5G Industrial IoT implementation commonly ask about deployment costs, network security, and integration with existing systems. Implementation expenses vary significantly based on facility size, existing infrastructure, and whether organizations choose private networks or carrier partnerships. Estimates for private 5G network deployment in medium-sized manufacturing facilities typically range from $500,000 to $2 million, including equipment, installation, and initial integration costs. Ongoing operational expenses depend on network management approaches and carrier service agreements. Security concerns are addressed through network slicing, encryption protocols, and isolated network architectures that prevent unauthorized access. Integration challenges exist when connecting legacy equipment to modern networks, often requiring gateway devices or protocol converters. Return on investment timelines generally span two to four years, depending on the scale of implementation and specific use cases. Organizations should conduct thorough assessments of their operational needs and existing infrastructure before committing to full-scale deployments.
| Implementation Aspect | Typical Range | Key Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Private Network Setup | $500K - $2M | Facility size, coverage area, equipment density |
| Network Equipment | $200K - $800K | Base stations, antennas, core network infrastructure |
| Device Integration | $100K - $500K | Sensors, gateways, edge computing devices |
| Annual Maintenance | $50K - $200K | Support contracts, software updates, network monitoring |
| ROI Timeline | 2-4 years | Depends on efficiency gains and reduced downtime |
Prices, rates, or cost estimates mentioned in this article are based on the latest available information but may change over time. Independent research is advised before making financial decisions.
The transformation enabled by 5G Industrial IoT extends beyond simple connectivity improvements. Organizations that successfully implement these systems report enhanced operational visibility, improved safety records, and increased competitive advantages through faster production cycles and higher quality standards. As the technology matures and deployment costs decrease, adoption across various industrial sectors continues to accelerate, establishing new benchmarks for manufacturing excellence and operational efficiency.